How Are Plant And Animal Cells Different?

In an ecosystem plants have the role of producers while animals have taken the role of consumers.
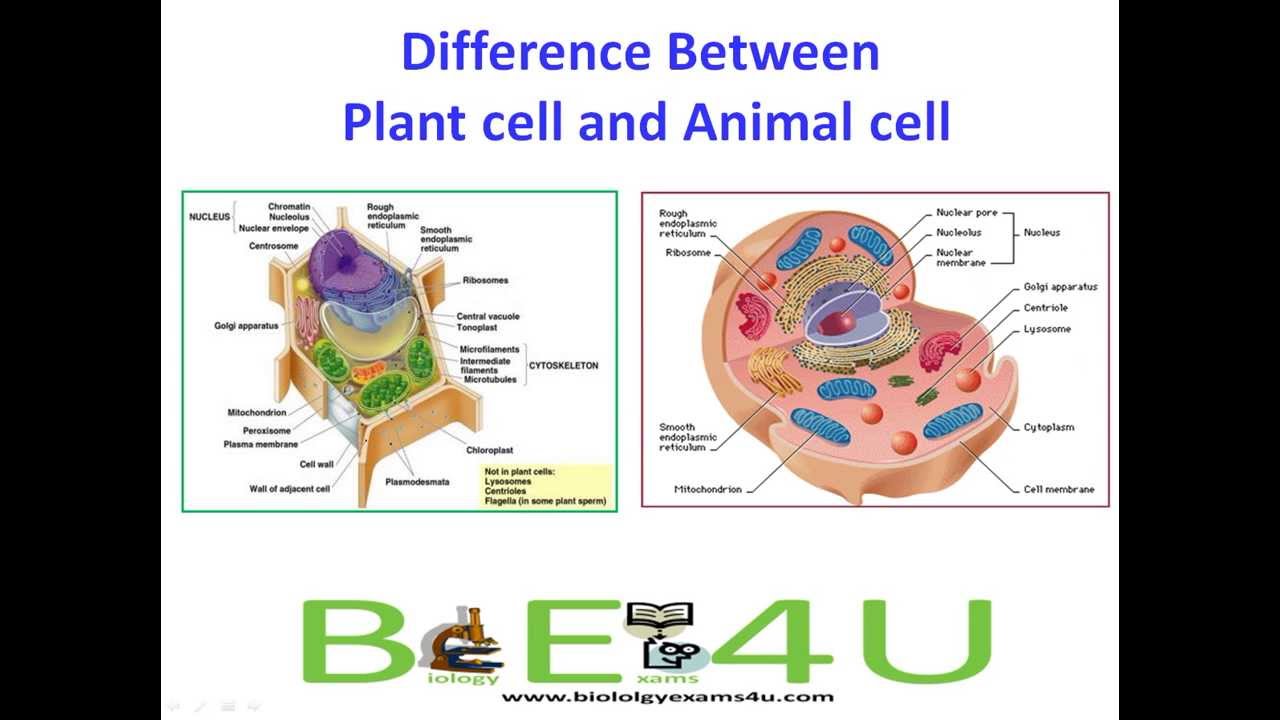
How are plant and animal cells different?. The main structural differences between plant and animal cells are the additional structures found in plant cells. Animal cells form a cleavage furrow. Like animal cells plant cells secret extracellular vesicles 191.
Isolated extracellular vesicles were found to contain small RNA species 184192 suggesting that they serve as a carrier of. Plant cells do not change shape before cell division. B Plant cells form a cell plate containing cell-wall building blocks.
Most human cells are produced by mitotic cell division with exception of gametes sperm and egg cells which are produced by meiosis. Most animal cells undergo a shape change referred to as mitotic cell rounding to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. These cells lack a cell wall plastids and other cellular organelles.
Animal cells are able to acquire carbohydrates for example by eating other organisms. The cells of multicellular animals and plants must also differentiate so that its cells develop features that enable them to fulfil specific roles. In plant cell cytokinesis cell plate formation takes place to.
Even though their cells are constructed similarly plants and animals have different cellular. Each type is specialised for a particular. Animal cells are mostly round and irregular in shape while plant cells have fixed rectangular shapes.
A The contractile filaments found in plant cells are structures composed of carbohydrates. A plant cell contains a large singular vacuole that is used for storage of water and nutrients. Both plant and animal cells have vacuoles.